A Master of Business Administration (MBA) in Information Technology (IT) and Fintech is a postgraduate degree focusing on subjects relevant to Information Technology and Fintech. E.g., Financial Management, Digital Innovation and Transformation, Machine Learning in Financial Analysis, etc. The study of IT has been around for quite some time now, and financial technology (fintech) is a relatively new field that encompasses studying new technologies to improve financial operations. You can opt for an MBA in IT and Fintech from any of the recognised institutions that provide the option of taking this course online or on-campus.
The demand for innovative technologies and IT in the financial sector is growing faster than ever, and our systems need to be more efficient, secure and streamlined. Many employers prefer a candidate with an MBA in IT and Fintech for job roles like Business Intelligence analysts, Financial Analysts, Machine Learning Experts, etc. Read the article to learn what to study in an MBA Finance and IT and important MBA finance topics.
MBA in IT and Fintech subjects
The common subjects in the MBA finance and IT course are:
- Information security management: This subject teaches about the basic principles and concepts of information security and the various approaches to safeguard your digital assets and networks. It ensures the protection of the confidentiality, integrity and availability of financial assets that are accessed by digital means.
- Financial management: It encompasses processes like planning, sorting, directing, and controlling the financial operations of an organisation. One of the essential financial management activities includes the collection and usage of funds efficiently.
- Web-based systems development: This subject aims to teach the students about the methods of designing and developing a web-based system. You will use the methods learned in this course to implement them in the financial sector.
- Big data and machine learning: Big Data is a term that describes very large and difficult-to-manage data, and it could be structured or unstructured. On the other hand, Machine Learning deals with a component of Artificial Intelligence that enables computers to adapt, learn, and improve using the available past data.
- FinTech: Fintech is short for Financial Technology and describes innovative technologies that aim to enhance and automate the usage and delivery of financial products and services.
- Corporate restructuring and Business valuation: Corporate Restructuring implies rearranging business operations and activities to increase profitability and efficiency. On the other hand, business valuation is the process of evaluating an organisation’s economic value or a unit.
- Investment analysis and portfolio management: Investment analysis is the process of researching and assessing an industry or a stock to determine how it will perform and if it fits a certain investor. Portfolio Management is the process of building and assessing a set of investment products that aims to fit a particular investor’s long-term financial objectives and risk tolerance.
- Banking and risk management: Many types of risk are associated with the banking industry. Some of the risks are credit risk, operational risk, liquidity risk, etc. This subject deals with the introduction to the types of threats and teaches about ways to mitigate them.
- Financial modelling: It is an important subject in the MBA in fintech syllabus. This subject deals with summarising an organisation’s expenses and revenue in a spreadsheet which can be further used to predict the impact of a future event.
- Strategy management: This subject deals with the process of planning, overseeing, analysing, and assessing an organisation’s important activities that are essential to achieving its overall objectives.
Get to know the complete syllabus of MBA IT and Fintech course
Some salient IT and Fintech concepts you must acquaint yourself with
Some of the top MBA in IT and fintech concepts that you must learn during your MBA programme are as follows:
Database management systems
Database Management Systems (DBMS) encompass modern ways of managing data storage requirements. With the advent of technological innovation and the internet, the rate of data generation has increased rapidly, and the data storage requirements have evolved from gigabytes to exabytes. To give you a perspective about it, one exabyte is equivalent to one billion gigabytes.
a database is an organised collection of data stored and accessed electronically. A Database Management System is the software technology used to create and manage these databases. It is also used to organise (retrieve, input, alter, delete, etc.) the data in a database. A few common examples of Database Management Systems are SQL Server, MySQL, Oracle, etc. A DBMS has the following major components:
- Hardware: It is the computer system used to access the database. The hardware can range from mainframes to microcomputers.
- Software: The software helps to set up a link between the database and the end users.
- Procedure: All the commands written on the DBMS software can be considered procedures.
- Data: Data is the set of information that is stored and managed by the DBMS.
- The language used to access the database: As with all other computer software, you need a specialised language to interact with the DBMS, known as the Database Access language. Using the database access language, you can perform functions on datasets like retrieve, input, alter, delete, etc.
Technology management
Technology Management is an umbrella term for interdisciplinary fields that enable organisations to manage their technology assets for competitive advantage. Organisations need to recognise the role of technology in all the individual departments and as an entire entity. Organisations should also invest in obtaining new technologies and upgrading existing technologies to improve them. Technology Management heavily depends on the organisation’s comprehension of technical and business skills.
Some of the advantages of investing in technology and technology management are as follows:
- Security and support: Technological advancements enable companies to automate the process of data storage and inventory storage. It will lower costs and boost productivity. It also helps them to secure their information with the use of encryption.
- Globalisation: Communication technologies enable businesses to have a global outreach and establish the commerce of products and services worldwide. Technological advancement is one of the significant causes of globalisation.
- Cloud computing: This technology enables many organisations to outsource a significant chunk of their activities to other parts of the world via the internet. Organisations that rely on cloud computing do not worry about crashes, downtime, or data storage.
- Targeting customers: Technological advancements create a significant shift in consumer trends. E.g. The advancement of the internet has opened doors to online marketplaces, which have the potential to make more profits than traditional marketplaces generally.
Cryptocurrency and blockchain
Cryptocurrency and Blockchain are two of the biggest buzzwords of this decade. Blockchain is a distributed ledger system which is open to everyone. Once the information is recorded in a block, it is challenging to modify it. In other words, a Blockchain can be perceived as a chain of blocks containing data. This technology was created mainly to timestamp digital documents to enhance their security. However, it was not used until 2009, when Satoshi Nakamoto created Cryptocurrency (known as Bitcoin) using blockchain technology.
cryptocurrency is an immutable, globalised, unbreakable and decentralised form of the existing currency system. It is a virtual currency that uses cryptography to work with the creator limiting the supply of cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency, and since then, several other cryptocurrencies (known as altcoins or alternative coins) have been created. E.g., Ethereum, Solana, Avalanche, etc.
IT strategy and management
IT Strategy (also known as technology strategy or IT technology strategic plan) can be defined as an elaborated plan that discusses how innovative technologies can be used to meet an organisation’s global business and IT objectives. It encompasses all the aspects of technology management, such as cost management, hardware management, software management, human capital management, vendor management and risk management. Planning and implementing an IT strategy in the financial sector requires lots of skills and expertise in the field of IT and Finance, and you can do so by pursuing an online MBA in IT and Fintech.
On the other hand, IT Management encompasses the process of monitoring and administering the IT systems of an organisation. The IT system includes the hardware, software and network systems, and IT Management emphasises how to make these IT systems more efficient. An essential part of the IT Management process is to plan and implement an IT strategy for the organisation.
Some other crucial tasks of an IT manager are:
- Ensuring that all the departments are receiving the sufficient technical support they need,
- Safeguarding the data and other digital assets of the company,
- Being up to date with the latest developments in the IT industry, etc
Enterprise resource planning
Enterprise Resource Planning (abbreviated ERP) is a multidisciplinary software solution that helps organisations to manage the various aspects of their business, such as customer relationship management (CRM), accounting, procurement, etc. It is a business management solution that aims to manage all aspects of a business operation via a centralised database and to enhance the efficiency of business operations via a user-friendly application interface.
Some of the advantages of Enterprise resource planning software are as follows:
- Single and centralised management of data: When you use enterprise resource planning software to operate your business, your data is managed within a single platform. It helps improve the consistency, accuracy, and security of your data.
- Data-driven decision-making: Enterprise resource planning software can also be used to create insightful, real-time, and analytical reports about your company. These reports contain metrics that can help you make data-driven decisions at all levels in your company.
- Regulatory compliance: Some industry-specific enterprise resource planning software has integrated compliance data which can be used to ensure that your operations and products are compliant with government regulations.
- Cost savings: As mentioned earlier, ERP is a multidisciplinary software that can help reduce the miscellaneous costs for business operations. In other words, you will not have to buy or subscribe to multiple tools. Some ERP tools offer profit and cost tracking features to monitor your budget.
- Streamlined operations and productivity: ERP software helps make business operations easier and more efficient. It aims to reduce repetitive activities and manual data entry tasks.
Banking and risk management
Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, monitoring, and mitigating the risks that could affect the global objectives of an organisation. It is also one of the essential MBA finance topics that helps to reduce risks in the banking domain.
Risk management in the banking sector can be defined as developing and implementing a plan to mitigate the risks associated with banking activities. It can be summed up with the following steps:
- Identification and evaluation of potential hazards in the banking sector
- Development and implementation of an action plan to mitigate these risks that could incur potential losses
- Assessment of the risk management process to make it better for future threats
Some of the risks associated with banking activities are as follows:
- Credit risk: It is the risk associated with a borrower who will not be able to pay back their loans or meet other obligations according to the pre-agreed terms.
- Liquidity risk: It is the risk of the bank’s inability to fulfil its cash and collateral commitments without bearing enormous losses.
- Market or systematic risk: It is the risk of incurring losses on investments due to certain factors such as increments in the interest rate, etc., that impact the banking sector’s overall performance.
- Operational risk: It is described as the risk of incurring losses on investments due to inefficient internal processes, systems and people. It could also be a result of external factors.
Financial markets and services
Financial markets is an umbrella term for any marketplace where people can trade financial products such as stocks, forex, bonds, derivatives, etc. It is an essential part of the MBA finance syllabus. Some common types of financial markets are as follows:
- Stock market: It is the most common type of financial market. These are the markets where businesses can list their company shares. Investors and traders can buy or sell these stocks to make money.
- Over the counter (OTC) market: A decentralised market where participants trade securities without a broker.
- Forex market: The market where traders can buy, sell, speculate, and hedge on the exchange rate of two different currencies.
- Money market: It helps trade products with a higher degree of safety and lower return on investment.
- Cryptocurrency market: It is the marketplace where cryptocurrency tokens are traded. These marketplaces offer digital wallets to traders to facilitate the exchange of cryptocurrencies.
Digital Innovation and transformation
Digital innovation is the implementation of modern digital technologies to resolve critical issues of an organisation. These technologies help the organisation to optimise business operations, improve customer experience, develop new business strategies, etc. Some great examples of digital innovation are Big data, Blockchain, Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), etc. Some examples of typical applications of these technologies are as follows:
- People use a mobile application that works on AR to measure distances between two points in the 3D space.
- Medical organisations trying to use AI to diagnose patients’ illnesses better.
- You can use a smartwatch to monitor your health-related metrics like daily steps, heart rate, etc.
Digital transformation, on the other hand, can be defined as the application of digital technologies in all business areas of an organisation. It helps to transform your business operations on every level and aims to provide greater value to your customers. It can also act as a cultural change that encourages businesses to promote innovations in their products by continually challenging the status quo, experimenting with new things, and learning from their failures.
Business intelligence and its tools
Business Intelligence (abbreviated as BI) is an umbrella term that consists of technology-driven processes used to analyse an organisation’s business data and gain valuable insights that the organisation can use to make data-driven decisions about its business operations. Some of the most important benefits of implementing business intelligence in your organisation are as follows:
- An improved decision-making process
- Streamlined business operations
- Enhanced operational efficiency
- A new source of revenue
- Competitive advantage over business competitors, etc
There are plenty of excellent business intelligence tools available online that you can opt for. The most commonly used tools are Microsoft Power BI, Tableau, etc. These tools can handle vast amounts of data and create insightful dashboards to visualise the data to help make data-driven decisions.
Organisations hire professional BI analysts and experts to work with their business data and the BI tool. An MBA in IT and Fintech can teach you about these concepts and help you better understand them to prepare you for a role in the Business Intelligence domain.
Advantages of doing an MBA in IT and Fintech
As explained in the above section, Fintech is a relatively new field that promotes implementing digital technologies in financial industries to modify and enhance the way traditional financial institutions function.
- An MBA in IT and Fintech prepares the students to understand how innovative technologies like Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT), Cloud Computing, Data Analytics, Data Science, Blockchain, etc. will help financial institutions to offer better and more efficient solutions to the customer, investors, and other stakeholders.
- As an MBA graduate in IT and Fintech, you will be able to understand the applications of Robo-advisory, insure-tech, algorithm trading and peer-to-peer lending in improving the efficiency of financial services.
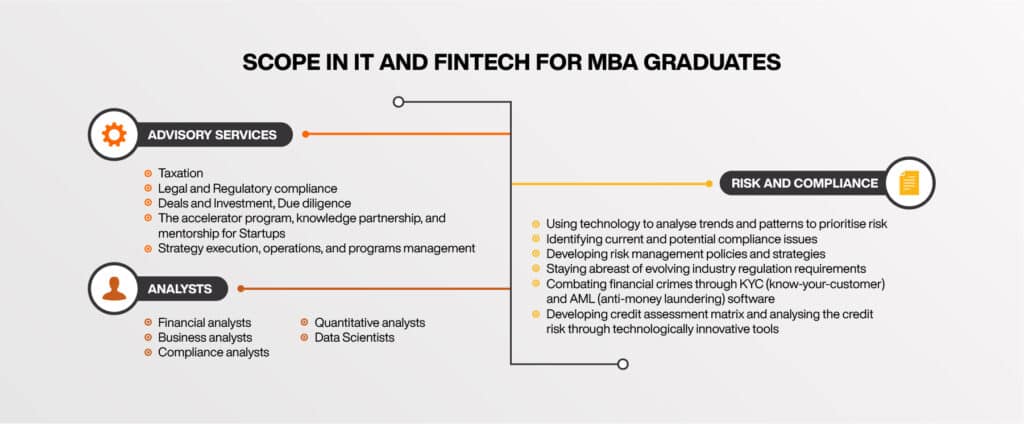
- The MBA Fintech syllabus will train the students to develop all the essential skills and behaviours to pursue a career in the Fintech industry. There are many career opportunities that you can pursue after finishing an MBA in IT and Fintech. We have listed some of the most attractive job profiles you can choose from after an MBA in IT and Fintech:
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies Developer
- Mobile Application Developer
- Cybersecurity Analyst
- Quantitative Analyst
- Risk and Compliance Officer
- Data Scientist
- Financial Analyst or Advisor
- Artificial Intelligence Engineer or Expert
- Product Manager
Learn how Fintech is transforming the Finance industry
In the earlier sections, we learned about some of the common products and services resulting from the developments in the Fintech industry. E.g., Digital Payments, Mobile-only (virtual) banks, Cryptocurrencies, etc. Statistically, it is estimated that two-thirds of the world’s adult population can manage to pay or receive a digital payment, with the share in developing economies growing from 35% in 2014 to 57% in 2021. The highest growth was witnessed in developing countries, with percentages of people using digital payment methods rising from 35 percent in 2014 to about 57 percent in 2021. It is just one example of the innovations driven by Fintech. Fintech is continuously transforming the Finance and Banking industry.
Now let us discuss how it is transforming the future of the finance and banking industry:
- Greater customer satisfaction: Most digital innovations in the finance industry align with customers’ expectations to provide customer satisfaction. E.g. Digital Banking offers a seamless experience to the customers. These modern technologies fulfil customer expectations by replacing outdated solutions with innovative digital ones.
- Enhanced compliance and security: Financial technologies can help banks and other financial institutions to navigate through rules, regulations and policies while safeguarding the assets and interests of all the stakeholders. For example, AI and machine learning help financial institutions detect anomalies and resolve them faster to ensure that cybersecurity is not compromised.
- More convenient: The fintech industry has streamlined the processes and activities in the financial and banking sector. Spending time on the tasks associated with investments, insurance, banking, etc., has become significantly easier to complete. The customers can perform a high level of analysis of existing data before making a new investment or trade. It is all because of the strides in the Fintech Industry.
- Possibility of decentralisation: The implementation of blockchain technology in the finance sector has given rise to the case of decentralised finance (abbreviated as DeFi). It is a system where an investor or trader, or consumer can interact with financial products and services on a decentralised blockchain network. It will remove the involvement of mediators like banks, broker-houses, and other financial institutions.
Also read the guide to get a job in the finance sector
Step up your game with an online MBA in IT and Fintech from Online Manipal
Online Manipal, the online platform by Manipal University Jaipur, offers an online Master of Business Administration degree with IT and Fintech as an elective. Manipal University Jaipur is a NAAC A+ accredited institution and offers UGC recognised courses. MBA in IT and Fintech from Online Manipal is a 2-year programme. The annual fee of this post-graduate course is INR 1,50,000, and you have the option to complete the payments in semester-wise instalments of INR 37,500. You can also choose other MBA electives, such as Human Resources Management (HRM), Marketing, Operations Management, Analytics and Data Science etc., as per your choice and interest.
After completing the MBA degree in IT and Finance, you will receive a course completion degree from Online Manipal that is rated highly by government institutions, private corporations, and startups. The institution offers placement assistance in the form of workshops to improve your CV, cover letter writing skills, and interview tips to land a lucrative job position. It also provides free access to Coursera so that students can learn and acquire all the necessary skills to succeed in their careers.
Conclusion
The demand for skilled professionals with a Master of Business Administration (MBA) in IT and Fintech has grown immensely in recent years. We see digital innovation in the field of finance in the form of cryptocurrencies, mobile payments, online banking, etc. You can learn the skills to pursue a career in Fintech by completing an online MBA from Online Manipal. You will learn about subjects belonging to both IT and Financial Technology, such as Information Security Management, Investment Analysis and Portfolio Management, Web-based systems development, Financial Management, etc.
Become future-ready with our online MBA program