Listen to this blog
What is an IPO?
IPO full form is Initial Public Offering. It can be defined as the first instance when a privately held company raises money by selling its securities and shares to the public. After the IPO, the issuing company is considered a public company.
This transformation of a private company into a public company is a crucial moment for private investors to cash in profit returns on their initial private investments. It is because an IPO consists of a share premium for existing private investors. But there are still many questions that remain like:
- How does a company go public?
- What are the benefits of going public?
- How can you invest in an IPO?
- Why do companies go for an IPO?
Read this blog post to learn more about the types of IPO, how an IPO works and investment opportunities with an IPO as an investor.
Types of IPO
The two common types of IPO are listed below:
- Fixed Price Offering
Fixed Price Offering is the type of IPO where the stock issuing company determines a fixed price for the initial sale of the shares. In this type of offering, the investors are informed of the price of the stocks before the company is made public. The demand for stocks from the share market can be determined after the issue is closed. The investors need to pay the full share price while filling out the application to participate in this type of IPO.
- Book Building Offering
Book Building Offering is the type of IPO where the stock issuing company offers a 20% price band on the share price to the investors. Then, the investors bid on the share price to determine the stock’s final price. The investors need to highlight the number of shares they want to purchase and the share price they are ready to pay. The Book Building Offering IPOs do not have a fixed price (like the Fixed Price Offering). In this type of IPO, the lowest price of the share is called the floor price and the highest price of the star is called the cap price. The final price of the share is finalised using the bids from investors.
Why do companies go public?
A private company considers going public for the following reasons:
- Raise funds: IPOs are a great way to raise funds for a private company. These funds can be used for business expansion, hiring, research and development, clearing debts, etc.
- Improve public image: The IPO process helps the company to be known in the Stock Market. It can help the company in business matters like valuation, mergers and acquisitions, etc.
- Valuation estimation: After listing the company’s stock, the company’s valuation can be determined based on the price per stock that the customer is willing to pay in the stock market.
- Improve credibility and trust: The IPO process boosts the trust among customers regarding the company and its products and services. It also improves the company’s credibility in the eyes of the governing financial body.
- Price transparency: The IPO process generates a lot of funds for the company, which will boost price transparency. The company can also create a liquid entity for the long-term shareholders.
Steps a company must take to go public via an IPO
Below are the five essential steps that a company must take to go public via an IPO:
- Hire an investment bank
The IPO issuing company must hire an investment bank for advisory and underwriting services. In the IPO process, investment banks act like intermediaries between the company and the public investors by providing underwriting services. The selection of bank is generally undertaken according to the following criteria:
- Industry domain expertise
- Prior engagements with the bank
- Quality of research carried out
- The reputation of the bank
- Security distribution ability
- Underwriting agreement and regulatory filings
The investment bank can have the following types of underwriting agreements with the issuing company:
- Best efforts agreement: This agreement doesn’t guarantee the amount raised through the IPO. The underwriter only partakes in the sale of securities for the company.
- Firm agreement: The investment bank guarantees a specific amount of funds raised in the IPO process under this agreement. The investment bank buys the entire offering and sells it to the public investor with adequate margins.
- All or none agreement: Under this agreement, the offer will be annulled if all the shares offered are not sold.
- Syndicate of underwriters: IPOs can be administered by multiple underwriters also. One of the investment banks will be appointed to head the other underwriters. Under this agreement, all the underwriters sell a portion of the shares offered by the issuing company. It is generally done to mitigate the risks involved in an IPO investment.
The underwriter(s) are in charge of curating all the documents listed below:
- Engagement letter: It consists of the reimbursement clause and the gross spread (also known as the underwriting discount).
- Letter of intent: It consists of the following details:
- The commitment by the underwriter to manage the IPO process of the issuing company.
- The issuing company’s commitment is to facilitate the underwriters with all the information required in the IPO process and collaborate in all the due diligence activities.
- The issuing company’s agreement is to offer a 15% over-allotment option to the underwriters.
- Underwriting agreement: This document comes into effect after the initial price of the securities is finalised.
- Registration statement: It consists of the IPO-related information, financial documents of the issuing company, insider holdings, background of the executive management of the company, legal cases against the issuing company, etc.
- Red Herring document: This document is the initial prospectus drafted by the underwriter, which consists of the information about the issuing company, the effective IPO date and the IPO price.
- Set the offering price
The IPO details need to be approved by the governing financial body (SEBI in India, SEC in the United States, etc.). After the approval, the date of the IPO is decided. The issuing company and the underwriter collaborate together to determine the offering price a day before the IPO date. The offering price is based on factors like economic stability in the market, the economic stability of the issuing company etc.
- After-market stabilisation
After the IPO is issued, the underwriter is responsible for performing market analysis and offering expert insights on after-market stabilisation to build a market for the shares distributed in the IPO.
- Transition to market competition
Now, the final step of becoming a public company is the transition to market competition. It generally starts 25 days after the IPO date. At this point, the underwriters offer data-driven insights about the fund collected and the final valuation of the issuing company.
How does a startup benefit from an IPO?
A startup can benefit from an IPO in the following ways:
- It offers access to a large pool of funds which can be used for business growth.
- It establishes diversity in the ownership of the shares of the company. This ensures that a few big investors aren’t calling the shots in the company.
- Startups receive positive publicity when their IPO is launched. This helps in improving the chances of acquisitions and takeovers.
- The company can now offer stock options to its employees after the listing of shares in the stock market.
- It is easier for companies to raise more money if they are listed public companies.
Can an IPO help a company grow?
An IPO process provides immense opportunities for growth to the companies. IPOs generate a large sum of capital that you can use for business expansion, hiring more employees, launching more product ranges, etc. Furthermore, the IPO process lists the company in the stock market, which improves the trust factor and credibility of the company. This will help the company to conduct business activities with other external entities. Finally, the funds collected from the IPO process help the company to have liquidity for future growth.
Should you invest in an IPO?
IPOs are very popular among public investors. This is because IPOs create volatile price fluctuations on the launch date of the IPO and some days after the launch. These volatile price fluctuations provide a great opportunity for investors to realise huge gains in the stock market. However, it can also bring huge losses.
Things to consider before investing in an IPO
Some important things to consider before investing in an IPO are as follows:
- There is a risk factor you need to consider before investing in an IPO. There is a chance that you might lose money in the investment.
- The income generated via the stock market is taxable.
- Applying to an IPO process doesn’t guarantee that you will receive the shares. There is a chance that you might not get the stock if your placed bid is lower than the IPO price.
- Make sure to read the prospectus before selecting the company and price per share.
Know if you’re eligible to invest in an IPO
You must fulfil the following eligibility criteria to invest in an IPO:
- The investor needs to have a Permanent Account Number.
- The investor needs to have a Valid Demat Account.
- If the investor is planning to sell the stocks on listings, he/she needs to have a trading account as well.
Steps to invest in an IPO
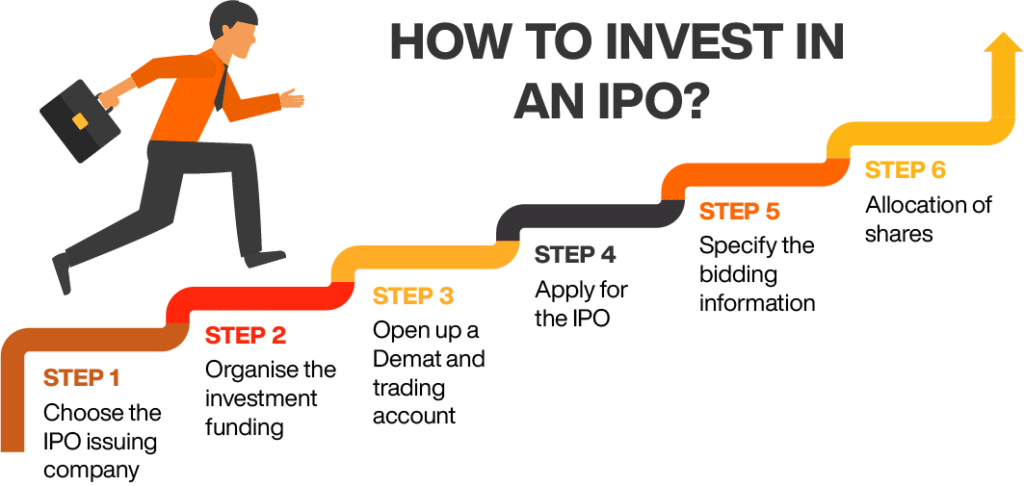
You need to take the following steps to invest in an IPO:
- Select the IPO issuing company: First, you need to select the company whose IPO shares you want to purchase. You can look into the initial prospectus and other information sources to determine the IPO issuing company.
- Manage the investment funding: Once you know which company’s shares you want to purchase, you need to manage the funds that will be needed to make the purchase.
- Open a Demat and trading account: The next step is to open a Demat account. You will not be able to apply for an IPO without a Demat account. It is highly recommended to open a trading account also along with the Demat account.
- Apply for the IPO: Now, you need to fill out the ASBA (Application Supported by Blocked Account) application forms. You also need to provide your Demat account details, Permanent Account Number, bidding information and bank account information in the application.
- Place your bid: In the last step, you need to specify your bidding information with the ASBA form.
- Allocation of shares: Finally, the shares will be allotted to the applicants in this step. The quality of shares allotted will depend on the supply and demand of the shares.
Advantages of investing in an IPO
Here are some of the advantages of investing in an IPO:
- Liquidity: Investors can sell their shares in the market to get liquid cash.
- Listing gains: When the price of the share increases on the day of listing, the investors can realise listing gains on their investment.
- Small retailers: Governing Financial Bodies make sure that small retail investors have a fair chance to participate in the IPO process.
- Cheap shares: The price of shares are generally the cheapest during the IPO stage. Hence, you can realise greater profits if you get an IPO.
- Shareholding: Anyone who purchases a share of a company is known as its shareholder. Some companies offer various benefits and perks to their shareholders.
How does an MBA in Finance teach about IPOs?
If you want to learn more about IPO and how it works, you can pursue an MBA in Finance from Manipal University Jaipur. Manipal University Jaipur is a NAAC A+ accredited university that offers UGC entitled MBA programme in Finance to its candidates. During this course, you will learn subjects like Accounting, Stock Market, Investment Banking, Portfolio Management, Business Analytics, etc.
An MBA in Finance can teach you everything you need to know about IPOs. The subjects and concepts taught in an MBA in Finance will help you gain expertise in the stock market and the IPO process. During your MBA in Finance, you will solve several case studies based on real data that will prepare you for investment opportunities in the future.
Also read: Guide to MBA in finance course
Conclusion
IPO or Initial Public Offering is defined as the time when a privately held company goes public by selling its shares to public investors. There are two main types of IPOs: Fixed Price offering and Book Building offering. The IPO process is beneficial for both the issuing company and the investors. You can consider applying for an MBA in Finance degree if you want to gain skills and knowledge relevant to the IPO process and the stock market. Manipal University Jaipur offers an online MBA Finance course with free access to Coursera, which you can use to develop skills needed to excel in the stock market.
Become future-ready with our online MBA program