Listen to this blog
If you’re thinking about taking a statistics class, you’ve undoubtedly wondered between a null hypothesis meaning and an alternative hypothesis meaning. Or you have come across the terms somewhere and may have wondered what is null hypothesis? What it accomplishes, and why it should be rejected. Or, for that matter, the alternative hypothesis definition.
The null hypothesis provides a relative statement about reality, while the alternative hypothesis provides a framework for reporting conclusions. This article will explain these principles and provide answers to your pressing queries. Continue reading to learn about the seven critical distinctions between a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis.
What is the Null Hypothesis?
Let’s start with what is a null hypothesis? The null hypothesis is a statistical phrase that refers to a scientist’s effort to disprove a specific hypothesis. When there are two conceivable outcomes, a null hypothesis is formed when the difference seen is attributable to chance alone.
A statistical test may compute the likelihood that the null hypothesis is correct, and its goal is to assess the probability that the observed difference is attributable to chance alone.
Null hypothesis principle
The null hypothesis asserts that there is no statistical link between two sets of variables. The null hypothesis may be applied to a single set of variables or two sets of variables. Scientists have a plethora of experiments at their disposal to test the null hypothesis.
They may go on to the other investigations after refuting the null hypothesis. The symbol H0 denotes the null hypothesis in statistics. It is also known as H-null or H-zero.
Purpose of null hypothesis
The null hypothesis is based on the premise that there are two alternative interpretations of a statistical relationship.
- According to the null hypothesis, the difference or ratio is zero when two groups are equal. The goal of null hypothesis testing is to assist researchers in determining which interpretation is more plausible.
- This test is often employed in scientific research, although its primary goal is to help researchers make reasoned decisions concerning statistical significance.
A sample mean test, for example, may be used to determine the mean of a population. In this scenario, the sample mean varies from the mean of the hypothetical population, but only in one direction.
The null hypothesis must be rejected when the sample mean deviates from the hypothetical population mean. However, a sample ‘mean’ deviation that is not predicted may be ruled out due to the absence of a substantial impact.
When should a null hypothesis be rejected?
The rejection of a null hypothesis has several ramifications.
- The first is that there is no evidence to support a null hypothesis. However, this does not rule out the existence of the impact, and in actuality, it may simply indicate that the sample size was insufficient. You must have an alternative hypothesis if you wish to reject a null hypothesis.
- A null hypothesis has no evidence to support it; that is, it does not withstand additional scrutiny. For example, research to see whether sunshine influences plant growth rates has yet to be undertaken using sunlight.
- Another research that analyses growth rates in the presence and absence of sunshine, on the other hand, would show that this is not the case. As a result, rejecting the null hypothesis opens the door to additional investigation. It does not imply that the experiment is pointless, but it does indicate that the research must continue.
- A test statistic must be calculated to determine if a null hypothesis is valid. This is the test statistic, and it is used to decide whether or not to reject the null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic exceeds the crucial value, and a rejection of the null hypothesis would be invalid otherwise.
- Furthermore, a test statistic that is less than the crucial value does not establish the presence of a null hypothesis.
Null hypothesis examples
A statistical hypothesis is referred to as a null hypothesis. The null hypothesis asserts that a specific condition must be disproven before you can accept that one particular effect exists.. As a result, H0 is the null hypothesis formula.
Here are some instances of how a null hypothesis may be used. Let’s have a look at two null hypothesis examples.
- The first is a medicine that lowers the chance of a heart stroke. The second scenario is if the treatment does not reduce the risk of heart stroke.
- In another example, a school principal asserts that a student’s average grade is seven out of ten. Assuming the population mean is 7.0, the null hypothesis is that students score seven out of ten on tests. The principal should keep track of the grades of 30 kids to evaluate this hypothesis, and then they should compute the sample mean and test the null hypothesis.
What is Alternative hypothesis?
An alternative hypothesis in statistics is a statement that relates two variables, often one variable from one group to another. The goal of the alternative view is to generate new ideas or information, and an alternative hypothesis should be straightforward and precise.
Unlike a null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis does not cite any outcomes supporting the idea, and it also may not imply complete assurance. To develop a compelling alternative hypothesis, you need to choose a collection of critical factors to investigate.
Furthermore, it should be verified within the time frame indicated to validate an alternative hypothesis. It should be straightforward to understand and offer a reference for its statement, and it should also explain why this is the case.
Alternative hypothesis principle
The principles of the alternative hypothesis are similar to those of the null hypothesis. In both cases, sufficient evidence must be obtained to support the researcher’s assumption. The data collected from a random sample are then processed through a statistical tool to measure how far the results deviate from the null hypothesis. A deviation of just a few percentages is acceptable; however, a variation of more than a factor of two is significant.
Purpose of alternative hypothesis
The objective of alternative hypothesis is to give a theory that is not the null hypothesis. The alternative hypothesis provides the researcher with a framework for presenting the study findings.
- The alternative hypothesis is utilised when the findings are inconsistent and the data does not support the null hypothesis. In this scenario, the researcher should provide an alternative hypothesis that includes facts that contradict the null hypothesis.
A researcher may devise a formula for the alternative hypothesis, often known as H1 or Ha. Then he may use this calculation to determine whether or not the alternative hypothesis is supported.
- The kind of test determines the alternative hypothesis’s aim. A one-tailed alternative idea looks for differences that are only in one way. In contrast, a two-tailed alternative hypothesis looks for differences in both directions.
The alternative hypothesis is valid if both alternative hypotheses are rejected. The two-tailed directional alternative hypothesis is concerned with two aspects of the distribution. It is widely employed in investigations when data from a large sample supports a hypothesis.
When should an alternative hypothesis be rejected?
When there is no evidence of a relationship between the variables in a population, the response is when the null hypothesis is true.
- The alternative hypothesis would imply a link between the variables in the population and the variables in the sample. If the alternative hypothesis is correct, the null hypothesis is not rejected.
- It is preferable to test a different hypothesis. The greater the evidence supporting the null hypothesis, the better the alternative hypothesis.
- Although failure to reject a null hypothesis is a typical statistical error, it does not always imply that an effect does not exist. Instead, it indicates that the sample size was insufficient or that the research overlooked something.
- Accepting a null hypothesis is also not statistically accurate. If you don’t know the answer to this question, think about a few more ways to test the null hypothesis.
Alternative hypothesis examples
These are critical features of alternative hypothesis examples. Following are some examples:
- Assume you’re a statistics student at a large high school. You think that students sleep less than the general population. If this is the case, you may put your idea to the test by utilising population data as your alternative hypothesis.
- Second, imagine you’re attempting to figure out what’s causing poor test results in primary schools. Assume you discover that pupils receive fewer than eight hours of sleep every night. If the evidence shows that the reverse is true, you’ll have a plausible alternative hypothesis. Alternatively, you may have discovered that poor classroom ventilation resulted in a low exam score. Whatever the cause, you’ll need to collect statistically significant data to support your hypothesis.
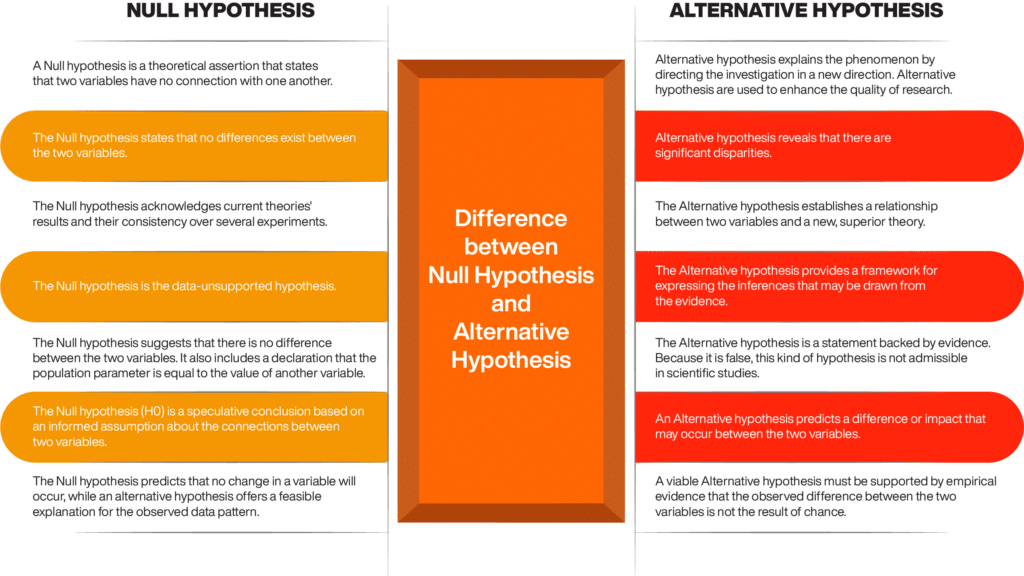
Null hypothesis vs alternative hypothesis: A comparison
A null hypothesis is a statistical supposition stating no difference between two variables in a population of between two groups of individuals. As a result, distinguishing between the Null and alternative hypothesis is critical.
Using the Null hypothesis and Alternative hypothesis examples, you may find that the null hypothesis is the most likely to be accurate, but its rejection does not necessarily indicate it erroneously. On the other hand, the alternative hypothesis asserts differences between the two variables, and the data supports this assertion.
Let us now look into the difference between the Null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.
Earn an MBA degree from Online Manipal
The online mode of learning an MBA is the choice of many working professionals these days. It is more comfortable for individuals to attend classes at their own pace and convenience, and it also cost-effective. With the pandemic outbreak, the necessity of online schooling has grown. Online MBA courses provided by institutions such as Manipal University Jaipur through the Online Manipal platform are advantageous and allow students to flourish in their careers.
Manipal University Jaipur’s online MBA courses are widely approved by corporations, government agencies, and higher education institutions. The course includes live instructor-led sessions and online proctored tests. The online courses provided by the university are equal to those taught on-campus.
Conclusion
When it comes to statistical data analysis, the null hypothesis is false. If it is, however, the alternative theory is correct. This signifies that the research is not a null hypothesis, and the findings are the outcome of a different hypothesis. The alternative hypothesis is a theory that differs from the null hypothesis in terms of statistical significance.
This post covered the difference between a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis, and why you would want to utilise it in your data analysis. Understand the principles and fundamentals of the null and alternative hypothesis as this will undoubtedly assist you in using the hypothesis as a tool in your study.
Prepare for your next career milestone with us